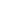
Sobre Mí
In the expansive ecosystem of Amazon Web Providers (AWS), Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) stands tall as probably the most fundamental and versatile services. Within EC2, Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) function the blueprints for virtual machines, providing the foundation for cases that power numerous workloads. When delving into EC2, understanding the two primary AMI types – those backed by Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) and people using Occasion Store – is essential for optimizing performance, resilience, and price-effectiveness.
Exploring AMI Types
EBS-backed AMIs:
Amazon EBS-backed AMIs are tightly integrated with Amazon's Elastic Block Store, a scalable block storage service designed for EC2 instances. These AMIs store their root gadget volume on Amazon EBS, providing persistent storage that persists beyond the lifespan of the EC2 occasion itself.
Key Options:
Data Persistence: EBS-backed AMIs offer persistent storage, guaranteeing that data remains intact even if the EC2 instance is terminated. This makes them ideally suited for applications requiring long-term data storage and durability.
Snapshot Capabilities: EBS volumes will be simply snapshotted, allowing for efficient backups, replication, and catastrophe recovery strategies. This enables customers to create point-in-time snapshots of their volumes, providing a reliable backup mechanism for mission-critical data.
Flexible Sizing: With EBS-backed AMIs, customers can dynamically resize their EBS volumes, permitting for adjustments to storage capacity without the necessity for downtime or data migration.
Cost Efficiency: While EBS volumes incur additional prices past the EC2 occasion usage, they offer price-efficient storage options compared to Occasion Store volumes for workloads requiring persistent data.
Occasion Store-backed AMIs:
In contrast, Instance Store-backed AMIs utilize ephemeral storage directly attached to the EC2 instance. This storage is physically linked to the host server and is not persistent – data stored on Occasion Store volumes is lost upon termination of the related EC2 instance.
Key Options:
High Performance: Occasion Store volumes often provide higher throughput and lower latency compared to EBS volumes since they're directly attached to the undermendacity hardware. This makes them suitable for applications requiring high-speed, non permanent storage.
No Additional Price: Unlike EBS volumes, which incur additional expenses, Instance Store volumes are included within the pricing of the EC2 instance. This makes them price-effective for short-lived workloads or applications that can tolerate data loss.
Very best for Non permanent Workloads: Occasion Store-backed AMIs are well-suited for stateless applications, batch processing, and momentary workloads where data persistence isn't a requirement. Examples embody cache servers, transient computing tasks, and high-performance computing (HPC) clusters.
Selecting the Proper AMI Type
Selecting the appropriate AMI type depends on the specific requirements of your workload, considering factors corresponding to performance, data persistence, scalability, and cost.
Persistence Requirements: If your application requires data persistence beyond the lifespan of individual EC2 situations or necessitates frequent data backups and snapshots, opting for an EBS-backed AMI is advisable.
Performance Considerations: For applications demanding high-speed, ephemeral storage with no want for data persistence, Occasion Store-backed AMIs offer superior performance and cost-efficiency.
Price Optimization: Understanding the fee implications of storage is crucial. While Instance Store volumes are included within the pricing of EC2 situations and are thus cost-effective for short-lived workloads, EBS volumes incur additional fees based mostly on usage.
Application Characteristics: Consider the nature of your application and its data requirements. Stateful applications or databases typically benefit from the durability and flexibility of EBS-backed storage, while stateless or transient workloads might leverage the performance advantages of Occasion Store volumes.
Conclusion
In the realm of Amazon EC2, choosing the proper AMI type – whether or not EBS-backed or Instance Store-backed – is essential for optimizing performance, resilience, and price-effectiveness. By understanding the traits and trade-offs related with every type, users can make informed decisions that align with the distinctive requirements of their workloads. Whether or not prioritizing data persistence, high performance, or cost efficiency, leveraging the appropriate AMI type is integral to unlocking the complete potential of Amazon EC2 and AWS as a whole.
Ubicación
Ocupación
Último Mensaje: 买加拿大假文凭Q微936794295,购买UPEI爱德华王子岛大学文凭毕业证,哪里有卖爱德华王子岛大学学历学位证明,购买加拿大大学烫金毕业证钢印文凭证书,海外留学成绩单假学历购买University of Prince Edward Island UPEI毕业证 Nuestro miembro más reciente: mindatiemann244 Últimos Mensajes Publicaciones sin leer Etiquetas
Iconos del foro: El foro no contiene publicaciones sin leer El foro contiene publicaciones sin leer
Iconos de los Temas: No respondidos Respondido Activo Popular Fijo No aprobados Resuelto Privado Cerrado