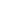
Sobre Mí
Canine osteoarthritis, additionally known as degenerative joint disease, is a common condition affecting dogs, particularly as they age. This degenerative condition can cause pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility in affected pets. Nevertheless, with proper management and care, pet owners can significantly improve their furry friend's quality of life. In this complete guide, we'll explore the assorted features of managing canine osteoarthritis to help pet owners navigate this challenging condition.
Understanding Canine Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis in dogs happens when the cartilage within their joints deteriorates over time, leading to irritation, pain, and stiffness. This degenerative process can result from varied factors, including age, genetics, obesity, joint accidents, and developmental disorders. Large breeds and chubby dogs are particularly prone to growing osteoarthritis.
Signs of canine osteoarthritis may embrace limping, reluctance to move, stiffness, decreased activity levels, issue rising, and behavioral modifications such as irritability or aggression because of discomfort. It's essential for pet owners to acknowledge these signs early on and seek veterinary care promptly.
Veterinary Assessment and Prognosis
If you suspect your dog could also be affected by osteoarthritis, seek the advice of with your veterinarian for a radical assessment. The veterinarian will perform a physical examination, overview the dog's medical history, and may recommend diagnostic tests similar to X-rays or joint fluid evaluation to confirm the prognosis and assess the severity of the condition.
Developing a Complete Management Plan
As soon as identified, the following step is to develop a complete management plan tailored to your dog's specific needs. This plan typically involves a mix of medical treatment, way of life modifications, weight management, and supportive care strategies.
Medicine: Veterinarians may prescribe varied drugs to manage pain and inflammation in dogs with osteoarthritis. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAIDs), similar to carprofen or meloxicam, are commonly used to alleviate discomfort and improve mobility. Additionally, supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate might help help joint health and cartilage repair.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for dogs with osteoarthritis, as extra weight places additional strain on their joints and exacerbates symptoms. Pet owners should work with their veterinarian to develop a balanced diet and train plan tailored to their dog's needs, aiming to achieve and maintain a perfect body condition score.
Physical Remedy and Exercise: Low-impact exercises, such as swimming or walking on soft surfaces, may also help improve muscle strength, joint flexibility, and total mobility in dogs with osteoarthritis. Physical therapy modalities like massage, stretching, and hydrotherapy may additionally provide therapeutic benefits and alleviate discomfort.
Environmental Modifications: Make adjustments to your own home environment to accommodate your arthritic dog's needs. Provide supportive bedding, ramps or steps for easy access to elevated surfaces, and slip-resistant flooring to prevent falls and injuries.
Various Therapies: In addition to traditional treatments, alternative therapies equivalent to acupuncture, laser remedy, and chiropractic care may supply additional pain relief and improve your dog's total well-being. Talk about these options with your veterinarian to determine their suitability on your pet.
Monitoring and Adjusting the Management Plan
Common monitoring and reevaluation of your dog's condition are essential to make sure that the management plan stays effective. Your veterinarian may need to adjust drugs, dosages, or treatment strategies based on your dog's response and any adjustments in their health status. Additionally, ongoing communication between pet owners and veterinary professionals is crucial for optimizing the management of canine osteoarthritis.
Conclusion
Managing canine osteoarthritis requires a multifaceted approach encompassing medical treatment, life-style modifications, and supportive care strategies. By working closely with your veterinarian and implementing a complete management plan, you possibly can assist alleviate your dog's pain, improve their mobility, and enhance their quality of life despite this challenging condition. Bear in mind to prioritize your pet's comfort and well-being, providing them with the love, support, and attention they should thrive despite osteoarthritis.
If you treasured this article and you simply would like to receive more info pertaining to librela nicely visit the internet site.
Ubicación
Ocupación
Último Mensaje: 买加拿大假文凭Q微936794295,购买UPEI爱德华王子岛大学文凭毕业证,哪里有卖爱德华王子岛大学学历学位证明,购买加拿大大学烫金毕业证钢印文凭证书,海外留学成绩单假学历购买University of Prince Edward Island UPEI毕业证 Nuestro miembro más reciente: burtonheydon700 Últimos Mensajes Publicaciones sin leer Etiquetas
Iconos del foro: El foro no contiene publicaciones sin leer El foro contiene publicaciones sin leer
Iconos de los Temas: No respondidos Respondido Activo Popular Fijo No aprobados Resuelto Privado Cerrado